Tεtrαctys ~ GEOMETRY ~ PYTHAGORAS/PYTHAGORUS
At 582 BC the Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras, from which we got the Pythagorean Theorem in geometry, once called the tetractys the symbol of the musical, arithmetic and geometric ratios upon which the universe is built. For Pythagoras and his followers, each line of the tetractys holds these meanings:
The Tetractys was considered a divine blueprint of creation and found many uses in Math, Medicine, Music, etc.
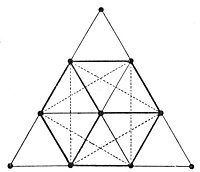
The Tetractys contains four rows with a successive number of dots 1, 2, 3, and 4, hence the name Tetractys.
The decimal numbers 0-9 can be assigned to each of the ten dots that form an equilateral triangle.
In the center we find the lowest number zero, that represents unrealized potential.
Zero was the source of all that came into being, represented by the highest number nine.
Nine thus represents All-One-ness, At-One-ment.
Since nine wanted to create other things it had to divide itself into two parts: six and three.
Six represents form, memory, and space. Three represents action, change, and life.
The interaction between six and three mediated by nine resulted in a further division into seven.
The six plus one numbers 1, 2, 4, 8, 7, 5, 10 form an eternal interplay supported and guided by the divine trinity 3,6, and 9.
The infinity pattern that connects the seven numbers 1, 2, 4, 8, 7, 5, 10 is based on Pythagorian musical tuning.
Each of the seven numbers represents a musical note and the full arrows connect two successive notes with ratio 9/8.
These notes and ratios (Platonic Lambda) are described in the Timaeus by Plato, another Greek philosopher.
The interrupted arrows connect two successive notes with a different ratio.
First row. The first row is made of a single point. This point is the divine dimension from which everything is created. Because of the nature of this point, it is usually associated with the virtue of wisdom.
Second row. The second row is a line connecting two points and signifies the first dimension. For the Pythagoreans, the second row represents “Neikos” or Strife. Strife is the power of division and is often associated with the virtues of movement and impulse. Movement and impulse, in turn, gives birth to courage and strength.
Third row. The third row is a line connecting three points. It is a representation of the second dimension and of “Philotes” or Harmony. Harmony is the marriage of physical beauty and mental balance.
Fourth row. The four points connected in the fourth row indicates the four elements of the ancient world: earth, air, fire and water.
Pythagoreans used to swear upon the tetractys in their hopes of attaining purity of mind and harnessing its power.

The sides of the Tetractys have the values 1 2 3 4 9 8 27, which are called "the seven boundaries of all numbers" (Mead 164); arranged in this way they are called the Lambdoma or Platonic Lambda. Their significance is described below.
In addition to the Tetractys that increases by addition, 1 2 3 4, the Pythagoreans say there is another that increases by multiplication, that is, in geometric proportion. Plato (Tim. 31C) says that a continuous geometric proportion is the most perfect bond, and so we find such a proportion along both sides of the Lambdoma: 1 2 4 8 and 1 3 9 27.
The duple progression (1 2 4 8) represents "the evolution of the vehicle" proceeding out of Unity, that is, the differentiation and division that constitute the physical body. The triple progression (1 3 9 27), in the order of involution (27 9 3 1), represents "the development of consciousness" as a return to unity, that is, the unification and integration of the psyche. (Note that the Pythagoreans considered 1 to be neither even nor odd, nor even a number properly speaking, but the source of both the even and odd numbers; 2 was the first even and 3 the first odd.) In general, the duple axis represents the physical, temporal, divisible and perishable; the triple axis represents the incorporeal, eternal, indivisible and imperishable.
The sides of the Tetractys have the values 1 2 3 4 9 8 27, which are called "the seven boundaries of all numbers" (Mead 164); arranged in this way they are called the Lambdoma or Platonic Lambda. Their significance is described below.
In addition to the Tetractys that increases by addition, 1 2 3 4, the Pythagoreans say there is another that increases by multiplication, that is, in geometric proportion. Plato (Tim. 31C) says that a continuous geometric proportion is the most perfect bond, and so we find such a proportion along both sides of the Lambdoma: 1 2 4 8 and 1 3 9 27.
The duple progression (1 2 4 8) represents "the evolution of the vehicle" proceeding out of Unity, that is, the differentiation and division that constitute the physical body. The triple progression (1 3 9 27), in the order of involution (27 9 3 1), represents "the development of consciousness" as a return to unity, that is, the unification and integration of the psyche. (Note that the Pythagoreans considered 1 to be neither even nor odd, nor even a number properly speaking, but the source of both the even and odd numbers; 2 was the first even and 3 the first odd.) In general, the duple axis represents the physical, temporal, divisible and perishable; the triple axis represents the incorporeal, eternal, indivisible and imperishable.
(Aristides III.24; Mead 165-8; Theon II.38)
The Emanations
Emanation IThe first emanation is the Monad (1), the plane of nondifferentiation, which is called the Seed (Sperma) and Root (Rhiza); it is the source and latent power of growth, and corresponds to a geometric point.
Emanation IIThe second emanation takes place when the point moves, generating a line, which is called Growth (Auxe); the value 2 corresponds to a curved line and 3 to a straight line.
Emanation IIIThe third emanation takes place when the line moves, generating a surface, which is called Skin (Khroia); the value 4 corresponds to a curved surface and 9 to a flat surface.
Emanation IIIIThe fourth emanation takes place when the surface moves, generating a solid, which is called Body (Soma); the value 8 corresponds to a solid with curved surfaces and 27 to a solid with flat surfaces.
(Cornford, Pl. Cosm. 43-52; Plato, Tim. 31B-32C; Theon II.38)
The PlanesNow we consider the Tetractys proper; the numbers of the decad (i-x) are shown above their numerical values:

Empedocles (fr. 17) taught that there are two primal forces in the universe, Strife (Neikos) and Amity (Philotes), which are the motive power behind the motion of the elements and the progress of the soul. Strife is the power of division (2) and therefore governs the duple progression; Amity is the power of union (3) and therefore governs the triple progression. Both are necessary to the existence of the universe. Indeed, Aristides (II.17) assigned the duple progression to Ares and the triple progression to Aphrodite, but he also assigned the interior numbers (6 12 18) of the Tetractys to Hephaistos, the Divine Craftsman (Demiourgos) who bound together Ares and Aphrodite when they had once united. Therefore, we will consider the planes again and see how they are bound together by the interior numbers for, in addition to the sides of the Tetractys, its bottom, 8 12 18 27, is bound together by geometric proportion, as is its center: 4 6 9, 2 6 18, and 3 6 12.)
Plane I
Plane II
Plane III
Plane IIII
Plane IThe first plane is the Monad (i) with numerical value 1, which the Pythagoreans consider neither even nor odd and neither prime nor composite. Wisdom is the virtue associated with the Monad, since it is integrative and at one with the Unus Mundus (we might say it moves in accord with the Tao). On it depend the Bodily Virtues in duple proportion (2 4 8) and the Psychic Virtues in triple proportion (3 9 27).
Plane IIThe second plane comprises the Dyad (ii) and Triad (iii), with numerical values 2 and 3. They are prime numbers, which means that their power is absolute and indivisible. Since these two potencies are indivisible (noncomposite), there can be no mean (reconciliation, harmonization) between them for, as Euclid proved, there can be no (geometric) mean between two prime numbers. This irreconcilable opposition is associated with impulse and movement; therefore the corresponding bodily virtue is strength (2) and the psychic virtue is courage (3).
Plane IIIThe third plane comprises the Tetrad, Pentad and Hexad (iv, v, vi), with numerical values 4, 6 and 9. The two extreme principles are square (surfaces) and divisible (4 = 2.2, 9 = 3.3), so each may give up a portion of its power to the other to create a (geometric) mean between them (6 = 2.3) for, as Euclid proved, there is a single mean between any two squares (surfaces). This plane corresponds to the psyche, for although it has extension, it has no thickness, and therefore cannot exist as a physical object, though it can be an image of a physical object.
The Pythagoreans considered the even numbers female and the odd numbers male, genders which can be interpreted as suggested by Aristotle (De Gen. & Cor. 716a14): the female is that which generates in itself, the male is that which generates in another. The value 6, corresponding to alchemical Mercury, represents the androgynous psyche as the mean between the female (4) and male (9) psyches, which correspond to alchemical salt and sulphur, respectively. The existence of a mean between the extremes represents good proportion (the Golden Mean), so the corresponding virtues are beauty (4) in the body and moderation (9) in the soul.
Plane IIIIThe fourth plane comprises the Heptad, Octad, Ennead and Decad (vii, viii, ix, x), with numerical values 8, 12, 18 and 27. The two extreme principles are cubic (solid) and divisible (8 = 2.2.2, 27 = 3.3.3); therefore there are two means between them (12 = 2.2.3, 18 = 2.3.3) for, as Euclid proved, there are two geometric means between two cubes (solids).
Since 2 represents the material principle and 3 the spiritual principle, we find that 8 is the number of earth and 27 is the number of fire, for Plato (Tim. 31B) said that physical objects presuppose three dimensions and are characterized by tangibility, which requires earth, and visibility, which requires fire. However, they cannot be united without a mean to join them, and indeed two means are required to join two cubic numbers. Thus the elements water (12) and air (18) are both necessary to physical unity.
The four elements, earth water air fire (8 12 18 27), are progressively less dense (material) and more subtle (spiritual). The extremes are absolutely dense (2.2.2) and absolutely subtle (3.3.3); the means are relatively dense (2.2.3) and relatively subtle (2.3.3). The subtle elements (air=2.3.3, fire=3.3.3) are both hot (separating), due to an excess of sulphur (3); the dense elements (earth=2.2.2, water=2.2.3) are both cold (coagulating), due to an excess of salt (2). The intermediate elements, water (12) and air (18), both contain mercury (6) as an exact divisor.
The elements satisfy two proportions: earth is to water as air is to fire (8:12 :: 18:27) - that is, as wet is to dry; and earth is to air as water is to fire (8:18 :: 12:27) - that is, as opposites. The four parts in double opposition (hot/cold, wet/dry) represent balance among parts (among the four there are six 3s and six 2s), and so the associated virtues are health (8) in the body and justice (27) in the soul.
(Aristides III.24; Cornford, Pl. Cos. 43-52; Plato, Tim. 31B-32C)
The Soul as Intermediate PlaneIn Platonic terms, Planes II, III and IIII represent three grades of existence. Plane II represents the indivisible existence of the Forms, which are intelligible, ungenerated, noncomposite, divine and eternal - the realm of Being. Plane IIII represents the divisible existence of Bodies or Things, which are perceptible, generated, composite, mundane and temporal - the realm of Becoming. Plane III represents the intermediate existence of Souls, which mixes Being and Becoming, the intelligible with the generated, in some ways noncomposite and in other ways composite. The Soul makes the world intelligible in time, for without change, life and intelligence is impossible.
As we've seen, Plane I is the Ineffable One. It is the pivot around which rotate the Axis of the Different (the duple progression) and the Axis of the Same (the triple progression), which rotate in opposite directions and together drive the universe and human experience. The Axis of the Different is the Erratic Cause, which is under the control of Nature (Physis) and moves by Chance (Tyche) and Necessity (Anangke); its rotation (counterclockwise from the Pole) causes cyclic generation and destruction; with it turn the Seven Planetary Spheres (for the planets have different motions). The Axis of the Same is the Inerratic Cause, which is under the control of Art (Techne), that is Reason and Design; its rotation (clockwise from the Pole) causes perpetual generation; with it turns the Astral Sphere (for the fixed stars all have the same motion). (Cornford, Pl. Cosm. 127-34, 141, 160-73; Plato, Tim. 47E-48B)
The three principles (4 6 9 = salt quicksilver sulphur) on the plane of the soul show its ways of apprehending the world. Along the axis of the divisible (1 2 4 8) it apprehends Intermediate Difference (represented by Salt = 4), that is, the mean between Formal Difference (2) and Physical Difference (8), which allows it to distinguish things. Along the axis of the indivisible (1 3 9 27) it apprehends Intermediate Sameness (represented by Sulphur = 9), that is, the mean between Formal Sameness (3) and Physical Sameness (27), which allows it to apprehend the identity of things. By combining the two it apprehends Intermediate Existence (represented by Quicksilver = 6), that is, existence in the psychic world. (Aristides III.11; Cornford, Pl. Cosm. 59-66; Plato, Tim. 35A)
More on the PlanesAccording to the Orphics, the contemplative virtues correspond to Plane I, which is supreme-at-one-ment; the spiritual virtues apply to Plane II, which is the causal body; the purifying virtues apply to Plane III, which is the subtle body; the practical virtues apply to Plane IIII, which is the gross body (Mead 181). Then again, according to Theon (II.38) and Aristotle (De An. 404b16ff), Plane I corresponds to the Mind (in unity), Plane II to science and knowledge (because they draw dualistic distinctions), Plane III to opinion (because it's a mean between knowledge and ignorance), and Plane IIII to sensation (there being four senses from which judgement proceeds: seeing, hearing, smelling and tasting). These are Jung's four functions: intuition, thinking, feeling and sensation.
Any geometric progression A:B:C:D generates a second geometric progression A : A+B : A+2B+C : A+3B+3C+D. In this way the "stationary progression" 1:1:1:1, representing the Unus Mundus, generates the duple progression 1:2:4:8, which in turn generates the triple progression 1:3:9:27. (Theon II.51)
Sources:
Aristides Quintilianus, De Musica, in A. Barker, Greek Musical Writings, Vol II: Harmonic and Acoustic Theory, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1989.
Cornford, F. M., Plato's Cosmology: The Timaeus of Plato Translated with a Running Commentary, London: Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1937.
Theon Smyrnaeus, Mathematics Useful for Understanding Plato, tr. R. & D. Lawlor, San Diego: Wizards Bookshelf, 1979.
~
ALSO: http://www.ka-gold-jewelry.com/p-articles/tetractis.php
~
AND: http://omegafoundation.siriuscomputing.net/Spirit/Tetractys.htm
Cornford, F. M., Plato's Cosmology: The Timaeus of Plato Translated with a Running Commentary, London: Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1937.
Theon Smyrnaeus, Mathematics Useful for Understanding Plato, tr. R. & D. Lawlor, San Diego: Wizards Bookshelf, 1979.
~
ALSO: http://www.ka-gold-jewelry.com/p-articles/tetractis.php
~
AND: http://omegafoundation.siriuscomputing.net/Spirit/Tetractys.htm


Comments
Post a Comment